
Lidar vs Radar vs Laser - Which technology fits your application?
LIDAR, Radar, and Laser scanners are all powerful technologies used to enhance safety in industrial and automated environments. But how do you choose the right one for your application?
OEM Automatic’s safety experts break down each technology to help you make an informed decision.
Learning hubLIDAR – How It Works
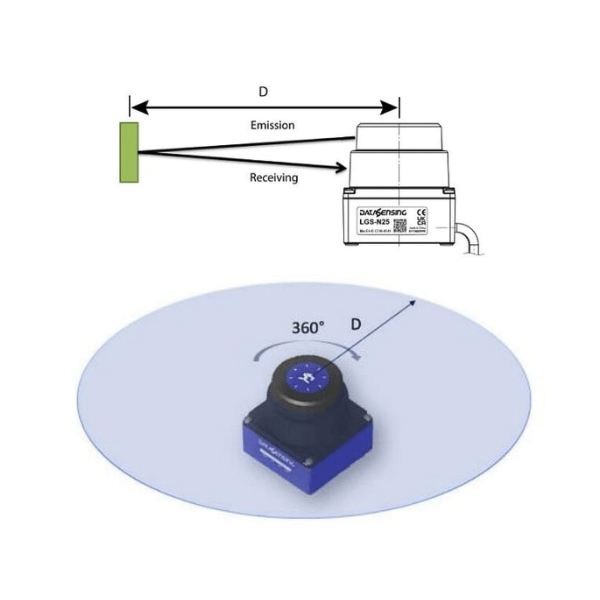
LIDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) uses laser-based time-of-flight (ToF) technology to construct a 360-degree view of the environment, usually used for measurement and navigation rather than safety. It emits laser pulses and measures the time it takes for each pulse to reflect off a surface and return to the sensor.
- Laser Emission – A short burst of light energy is emitted.
- Reflection/Return – The laser pulses bounce off objects or surfaces.
- Measurement – The time taken for the laser pulse to travel to and from the object is measured precisely.
- Calculation – Using the known speed of light and time of flight, the distance to each object is calculated.
- 3D Point Cloud – This process is repeated with multiple lasers from different angles to generate a collection of 3D data points known as a “point cloud.”
- Data Application – The point cloud data is processed to create a detailed model or visualisation of the scanned environment.
Radar – How It Works
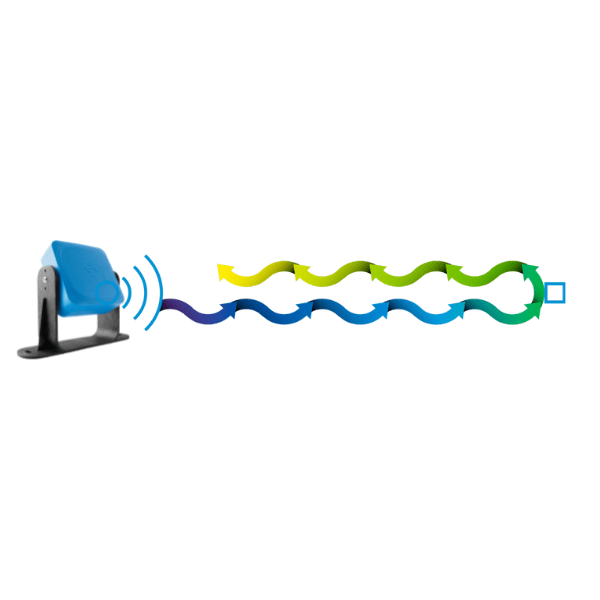
Radar (Radio Detection and Ranging) uses radio waves to detect the location, speed, and direction of objects. It works by emitting radio signals, which reflect off surfaces and return to the sensor.
- Radio Emission – A radar signal is transmitted, often as chirps or frequency-modulated continuous waves (FMCW).
- Reflection/Return – The signal reflects off objects within its range.
- Measurement – The reflected signals are received by the sensor.
- Calculation:
- Distance – Based on the time taken for the signal to return.
- Velocity – Calculated through the Doppler effect (frequency shift of the reflected wave).
- Direction – Determined by the angle of arrival of the reflected signal.
- Data Application – Radar data can be used to trigger safety protocols based on distance, speed, and direction of moving or stationary objects.
Laser – How It Works
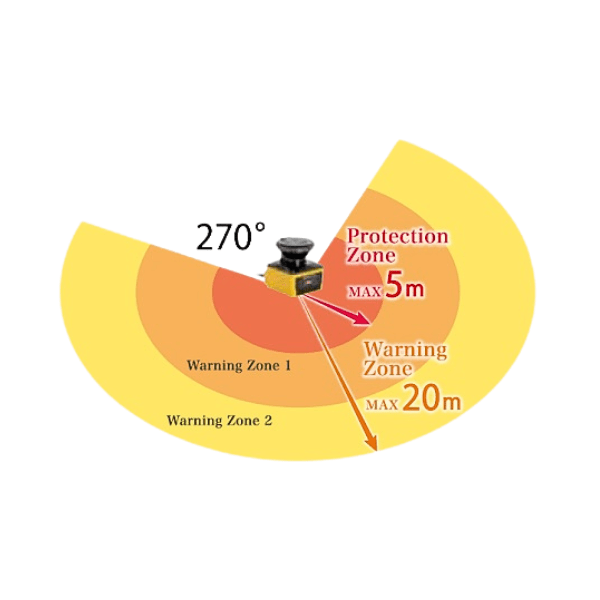
Laser scanners use focused infrared laser beams to scan a defined area, identifying the presence and distance of objects. They are commonly used in safety applications to monitor zones and prevent access to hazardous areas.
- Laser Emission – Infrared lasers are emitted in a fan-shaped pattern to cover a monitored area.
- Reflection/Return – The laser beam hits objects and reflects back to the sensor.
- Measurement – The time taken for the beam to return is measured.
- Calculation – Distance is calculated using the time of travel and the speed of light.
- Data Application – Depending on the programmed safety or warning zones, the scanner will trigger alerts or protective actions when thresholds are breached.
Advantages & Disadvantages of Lidar, Radar & Laser technology
LIDAR
Advantages:
- High Precision & Accuracy – Enables detailed 3D mapping and reliable object detection.
- High-Resolution Imaging – Captures complex environments in great detail.
- Ideal for Autonomous Vehicles – Supports precise navigation and environment modelling.
- Versatile – Applicable across diverse industries and use cases.
Disadvantages:
- High Cost – Typically more expensive to purchase and maintain.
- Sensitivity to Light – Performance may be affected by bright ambient light.
- Limited Range – Detection range is generally shorter than radar.
- Complex Data Handling – Requires advanced software and expertise to process large datasets.
- Safety – LIDAR is not safety certified but used more in navigation and measurement in AGV applications
Radar
Advantages:
- Long-Range Detection – Can detect objects at significant distances.
- Reliable in Adverse Conditions – Performs consistently in poor visibility (e.g., fog, steam, or spray).
- Consistent Measurements – Offers accurate and repeatable detection of speed and distance.
- Cost-Effective – More affordable than other technologies for many safety applications.
Disadvantages:
- Limited Small Object Detection – Struggles to identify small or closely positioned objects.
- Susceptibility to Interference – Signal accuracy can be affected by certain materials or environments.
- False Readings in Structured Tanks – May produce inaccurate data in confined or stratified environments.
- Cosine Effect & Angle Sensitivity – Less accurate speed measurement if not aligned directly with the object’s direction.
Laser
Advantages:
- Enhanced Safety Coverage – Creates protective safety fields for advanced area monitoring.
- Highly Versatile – Works in both stationary and mobile applications with flexible field configuration.
- Improved Ergonomics – Offers better space utilisation than traditional safety solutions.
- Non-Contact Measurement – Allows accurate sensing without physical contact.
Disadvantages:
- Environmental Sensitivity – Light, dust, or reflective surfaces may reduce accuracy.
- Field Setup Complexity – Incorrect zone configuration may compromise safety.
- Eye Safety Risks – Must be properly assessed and installed to avoid posing a risk to eye safety.
- Challenges with Transparent/Reflective Surfaces – May struggle to detect transparent or highly reflective materials reliably.
Typical Applications For Lidar, Radar & Laser Scanners

Lidar Scanner Applications
- Autonomous Vehicles - Environmental perception, object detection, and navigation
- AGVs (Automated Guided Vehicle) - Navigation in manufacturing and warehouse settings
- Robotics - Mapping, obstacle detection, and path planning
Radar Scanner Applications
- Industrial Robotics - Detecting eople and ojcts in automated workspaces
- Heavy Machinery - Monitoring zones around dangerous equipment
- Material Handling - Preventing accidents on conveyors and loading areas
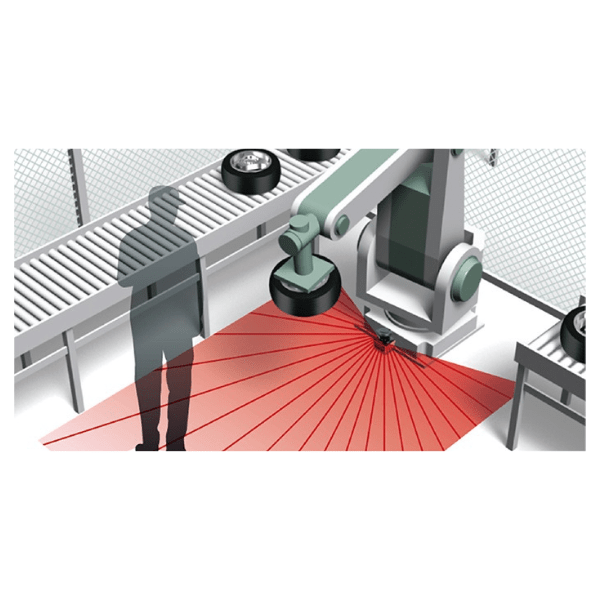
Laser Scanner Applications
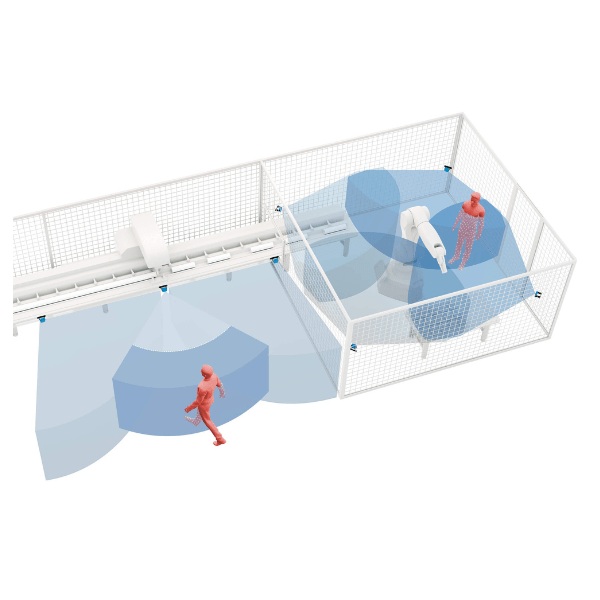
- Area Protection - Preventing access to hazardous zones during machine operation
- AGV Collision Avoidance - Detecting objects and people near moving vehicles
- Machine Safety - Triggering alarms or shutdowns when people enter danger zones
Summary
Lidar – perfect for navigation and measurement applications
Radar – safety in automated workspaces and material handling applications
Laser – protects using zones of safety, ideal for area and machine protection and AGV collision to trigger safety protocols such as shutdown.
Choosing a Trusted Manufacturer
At OEM Automatic, we supply high-quality LIDAR, Radar, and Laser scanners from trusted manufacturers including Datasensing, Hokuyo, and Inxpect. Each product is carefully selected to meet the diverse safety requirements of industrial applications.
Our safety specialists are here to help you select the ideal technology—whether it’s LIDAR, Radar, or Laser—based on your specific use case.
Need Help with a Scanner Application?
Our Sensors & Safety team is ready to assist with expert advice, product recommendations, and proof-of-concept support.
Phone: 0116 284 9900
Email: [email protected]
Live Chat: Available on our website
Onsite Support: Book a visit from one of our experienced engineers for demonstrations and application advice – email [email protected] to arrange a visit
Let us help you find the right technology for your application. Contact us today.
related products

Hokuyo UAM-05 Safety Laser Scanner
- Protection zone 5m
- Warning zone 20m
- Versatile scanner for various applications
- Type 3, SIL2, PLd

Datasensing - Safety Laser Scanner
Laser Sentinel Enhanced
- I/O connection
- More than 72m² safely monitored
- Up to 70 zone sets
- up to 3 simultaneous safety zones

Safety Radar S101A
Radar Sensor S101A
- Immune to smoke, dust and water splashes
- Can be used Outdoors
- -40 to +60°C
- SIL2, PLd
- 4m safety area

Safety Radar S201A
Radar Sensor S201A (MLR)
- Can work in dust, steam, smoke and when splashed with water
- 0.5m-9m safety zone
- Field of view adjustable from 10°-100°
- -30°C to +60 °C
- SIL 2, Pld

Safety Radar S203A
Radar Sensor S203A-W, S203A-WL
- Can work in dust, steam, smoke and when splashed with water
- 0.5m-9m safety zone
- 10°-100° Horizontal field of view
- Vertical spread 12°
- SIL 2, PLd

Datasensing LIDAR Collision Avoidance Guidance Scanner
LGS-A10
- Scanning Angle Of 360°
- Sensing Distance Up To 25 Meters
- For Collision Avoidance & Object Detection
- Based On Time-Of-Flight Infrared Laser Technology

Datasensing LIDAR Navigation Guidance Scanner
LGS-N50
- Scanning Angle Of 360°
- Sensing Distance Up To 50 Meters
- For Natural Or Marker Navigation For Automated Guided Vehicles
- Based On Time-Of-Flight Infrared Laser Technology

Datasensing LIDAR Compact Navigation Guidance Scanner
LGS-N25
- Scanning Angle Of 360°
- Distance Up To 25 Meters
- For Natural Navigation And Object Profiling
- Based On Time-Of-Flight Infrared Laser Technology



